

Delivers variable pressure to achieve targeted percentage of work of breathing.May be used to wean off patient after extubation (maybe combined with pressure support ventilation- PSV).
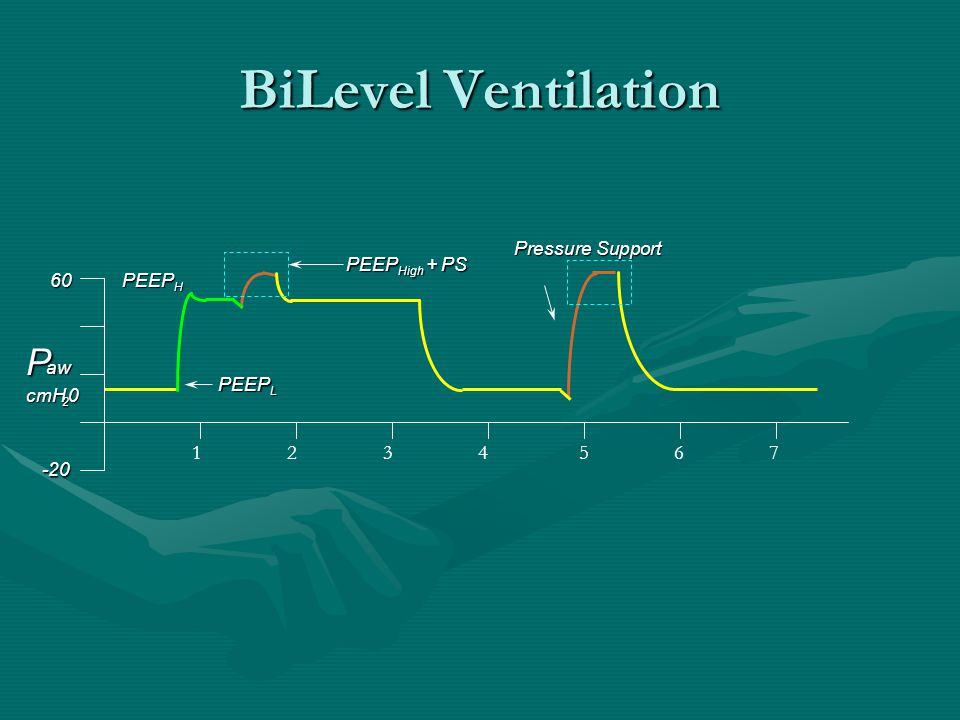
This strategy also supplies inspiratory pressure during spontaneous breaths (similar to pressure support ventilation).Tidal volume of additional breaths is determined by the patients effort.Ventilator develops a minimum number of supported breaths.Synchronous intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) If patient develops tachypnea, may lead to respiratory alkalosis, breath stacking and auto PEEP.May be pressure targeted or volume targeted.Therefore, vent-triggered breaths are identical to patient triggered breaths Additional patient initiated breaths trigger fully assisted vent breaths.Mode of fully assisted ventilatory support.Ventilator delivers a minimum number of supported breaths.The volume given depends upon the patient's effort and lung/ chest wall complianceĬontinued mandatory ventilation (CMV) or assist control (AC).After the optimal flow is achieved, the applied pressure can be turned off.The patient sets the respiratory rate and generates their desired flow rate. Mode of partial ventilatory support because there is no set rate.This mode supports patient initiated breaths with a set inspiratory pressure and positive end expiratory pressure ( PEEP).The following are the various ventilator modes and their features: Pressure support ventilation (PSV) In some conditions, for example in case of spontaneously breathing patient, the patient sets the respiratory rate and generates the desired flow rate.

Choice of ventilator mode can be tailored to achieve specific goals of management and set to achieve spontaneous breathing, volume-targeted ventilation, pressure-targeted ventilation, or some combination. Different modes of ventilation include pressure support ventilation (PSV), continued mandatory ventilation (CMV) or assist control mode (AC), synchronous intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV), proportional assist ventilation (PAV), dual control mode, high frequency ventilation, pressure and volume targeted modes.Ĭhoice of ventilator mode depends upon the clinical condition of the patient. Kazmi BSc, MD OverviewĬhoice of ventilator mode depends upon the clinical condition of the patient. Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Syed Hassan A. Risk calculators and risk factors for Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modesĮditor-In-Chief: C. Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modes in the newsīlogs on Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modesĭirections to Hospitals Treating Mechanical ventilation Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modes On the WebĪmerican Roentgen Ray Society Images of Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modesĪll Images X-rays Echo & Ultrasound CT Images MRIįDA on Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modesĬDC on Mechanical ventilation choosing amongst ventilator modes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
